3.2 KiB
RBF-aPID-Controller
RBF Neural Net Adaptive PID Controller
Implementations of a radial basis function (RBF) neural network adaptive PID controller. Uses neural net and error information from PID control to adapt the control signal.
Python Implementation
Developed to provide one adaptation value to the control signal
using the error, integral, and derivative terms. Done in TensorFlow and Numpy.
To adapt the PID gains instead of the control signal in TF, the network outputs
must be made to 3 neurons and added to the gains. In Numpy, the gains will need to
be added to inputs and the adapted signal added to the gains.
Example usage with simulated data can be found in first_order_sim.py.
Training data was simulated using the model itself for the TF Trained example. Each project
has its own testing suite using unittest. The tests can be run with run_np_tests.py
or run_tf_test.py.
# Run project tests separately from their implementations
python -m unittest discover -s test -p "*.py" -v
C++ Implementation
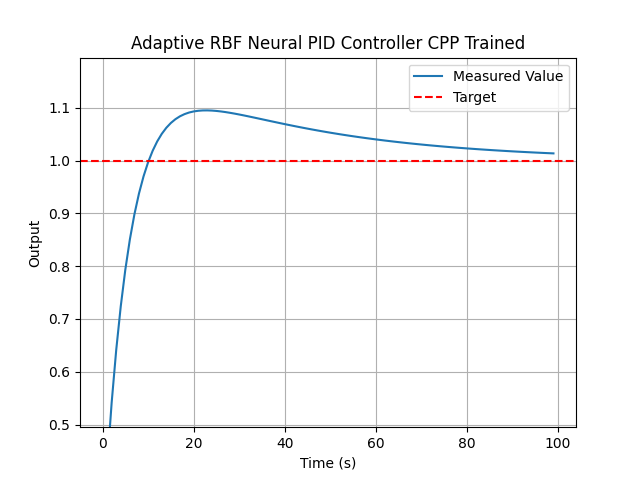
A hybrid method; uses the error and PID gains (Kp, Ki, and Kd) to adapt the control signal. This gives more flexibility to the control model as the gains can be easily adapted since the RBF model already learns from them. The dual inputs should provide greater stability to the system, but will be more sensitive to the gains. This system also actively adapts during usage.
The C++ implementation can already be used for any adaptation, adding the result of predict() to
whatever values are desired to adapt. Uses just the cmath and cstdlib libraries with memory
management handled manually as the system it was designed for could not import additional libraries.
cstdlib can be removed if you don't care about random initialization of the centers.
Example usage with simulated data can be found in main.cpp. It includes some additional libraries in order to show an example usage with a simple first order simulation. Training data was not simulated for the trained example, fake inputs were made.
The project uses CMake to build and create the main executable and test executable. Tests for the adaptive PID controller and RBF model are included using gtest.
An example CMake build:
mkdir build/
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
ctest // Run CMake test executable (all tests as one)
./control_system // Main executable with simulation output
./model_tests // Test executable to view all individual test outputs
Simulation examples from the three implementations:
- TF_Implementation: Using TensorFlow to build and train the RBF Model.
- NP_Implementation: Using Numpy to build and train the RBF Model.
- CPP_Implementation: Using C++ for embedded systems to build and train the RBF Model.