mirror of
https://github.com/odriverobotics/ODrive.git
synced 2026-02-09 00:42:43 +08:00
Added note about torque_constant to getting started page, added debugging info for firmware/odrivetool version mismatch to troubleshooting page, removed interfaces page and split it into sections under the interfaces section, added migration guide to tutorials section
This commit is contained in:
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
GEM
|
||||
remote: https://rubygems.org/
|
||||
specs:
|
||||
activesupport (6.0.3.1)
|
||||
activesupport (6.0.3.4)
|
||||
concurrent-ruby (~> 1.0, >= 1.0.2)
|
||||
i18n (>= 0.7, < 2)
|
||||
minitest (~> 5.1)
|
||||
@@ -16,10 +16,10 @@ GEM
|
||||
colorator (1.1.0)
|
||||
commonmarker (0.17.13)
|
||||
ruby-enum (~> 0.5)
|
||||
concurrent-ruby (1.1.6)
|
||||
dnsruby (1.61.3)
|
||||
addressable (~> 2.5)
|
||||
em-websocket (0.5.1)
|
||||
concurrent-ruby (1.1.7)
|
||||
dnsruby (1.61.4)
|
||||
simpleidn (~> 0.1)
|
||||
em-websocket (0.5.2)
|
||||
eventmachine (>= 0.12.9)
|
||||
http_parser.rb (~> 0.6.0)
|
||||
ethon (0.12.0)
|
||||
@@ -28,26 +28,26 @@ GEM
|
||||
execjs (2.7.0)
|
||||
faraday (1.0.1)
|
||||
multipart-post (>= 1.2, < 3)
|
||||
ffi (1.12.2)
|
||||
ffi (1.13.1)
|
||||
forwardable-extended (2.6.0)
|
||||
gemoji (3.0.1)
|
||||
github-pages (206)
|
||||
github-pages (209)
|
||||
github-pages-health-check (= 1.16.1)
|
||||
jekyll (= 3.8.7)
|
||||
jekyll (= 3.9.0)
|
||||
jekyll-avatar (= 0.7.0)
|
||||
jekyll-coffeescript (= 1.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-commonmark-ghpages (= 0.1.6)
|
||||
jekyll-default-layout (= 0.1.4)
|
||||
jekyll-feed (= 0.13.0)
|
||||
jekyll-feed (= 0.15.1)
|
||||
jekyll-gist (= 1.5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-github-metadata (= 2.13.0)
|
||||
jekyll-mentions (= 1.5.1)
|
||||
jekyll-mentions (= 1.6.0)
|
||||
jekyll-optional-front-matter (= 0.3.2)
|
||||
jekyll-paginate (= 1.1.0)
|
||||
jekyll-readme-index (= 0.3.0)
|
||||
jekyll-redirect-from (= 0.15.0)
|
||||
jekyll-redirect-from (= 0.16.0)
|
||||
jekyll-relative-links (= 0.6.1)
|
||||
jekyll-remote-theme (= 0.4.1)
|
||||
jekyll-remote-theme (= 0.4.2)
|
||||
jekyll-sass-converter (= 1.5.2)
|
||||
jekyll-seo-tag (= 2.6.1)
|
||||
jekyll-sitemap (= 1.4.0)
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll-theme-architect (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-cayman (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-dinky (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-hacker (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-hacker (= 0.1.2)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-leap-day (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-merlot (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-midnight (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
@@ -66,13 +66,14 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll-theme-tactile (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-time-machine (= 0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll-titles-from-headings (= 0.5.3)
|
||||
jemoji (= 0.11.1)
|
||||
kramdown (= 1.17.0)
|
||||
jemoji (= 0.12.0)
|
||||
kramdown (= 2.3.0)
|
||||
kramdown-parser-gfm (= 1.1.0)
|
||||
liquid (= 4.0.3)
|
||||
mercenary (~> 0.3)
|
||||
minima (= 2.5.1)
|
||||
nokogiri (>= 1.10.4, < 2.0)
|
||||
rouge (= 3.19.0)
|
||||
rouge (= 3.23.0)
|
||||
terminal-table (~> 1.4)
|
||||
github-pages-health-check (1.16.1)
|
||||
addressable (~> 2.3)
|
||||
@@ -80,20 +81,20 @@ GEM
|
||||
octokit (~> 4.0)
|
||||
public_suffix (~> 3.0)
|
||||
typhoeus (~> 1.3)
|
||||
html-pipeline (2.13.0)
|
||||
html-pipeline (2.14.0)
|
||||
activesupport (>= 2)
|
||||
nokogiri (>= 1.4)
|
||||
http_parser.rb (0.6.0)
|
||||
i18n (0.9.5)
|
||||
concurrent-ruby (~> 1.0)
|
||||
jekyll (3.8.7)
|
||||
jekyll (3.9.0)
|
||||
addressable (~> 2.4)
|
||||
colorator (~> 1.0)
|
||||
em-websocket (~> 0.5)
|
||||
i18n (~> 0.7)
|
||||
jekyll-sass-converter (~> 1.0)
|
||||
jekyll-watch (~> 2.0)
|
||||
kramdown (~> 1.14)
|
||||
kramdown (>= 1.17, < 3)
|
||||
liquid (~> 4.0)
|
||||
mercenary (~> 0.3.3)
|
||||
pathutil (~> 0.9)
|
||||
@@ -113,14 +114,14 @@ GEM
|
||||
rouge (>= 2.0, < 4.0)
|
||||
jekyll-default-layout (0.1.4)
|
||||
jekyll (~> 3.0)
|
||||
jekyll-feed (0.13.0)
|
||||
jekyll-feed (0.15.1)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.7, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-gist (1.5.0)
|
||||
octokit (~> 4.2)
|
||||
jekyll-github-metadata (2.13.0)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.4, < 5.0)
|
||||
octokit (~> 4.0, != 4.4.0)
|
||||
jekyll-mentions (1.5.1)
|
||||
jekyll-mentions (1.6.0)
|
||||
html-pipeline (~> 2.3)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.7, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-optional-front-matter (0.3.2)
|
||||
@@ -128,14 +129,15 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll-paginate (1.1.0)
|
||||
jekyll-readme-index (0.3.0)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.0, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-redirect-from (0.15.0)
|
||||
jekyll-redirect-from (0.16.0)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.3, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-relative-links (0.6.1)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.3, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-remote-theme (0.4.1)
|
||||
jekyll-remote-theme (0.4.2)
|
||||
addressable (~> 2.0)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.5, < 5.0)
|
||||
rubyzip (>= 1.3.0)
|
||||
jekyll-sass-converter (>= 1.0, <= 3.0.0, != 2.0.0)
|
||||
rubyzip (>= 1.3.0, < 3.0)
|
||||
jekyll-sass-converter (1.5.2)
|
||||
sass (~> 3.4)
|
||||
jekyll-seo-tag (2.6.1)
|
||||
@@ -152,8 +154,8 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll-theme-dinky (0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll (~> 3.5)
|
||||
jekyll-seo-tag (~> 2.0)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-hacker (0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll (~> 3.5)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-hacker (0.1.2)
|
||||
jekyll (> 3.5, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-seo-tag (~> 2.0)
|
||||
jekyll-theme-leap-day (0.1.1)
|
||||
jekyll (~> 3.5)
|
||||
@@ -187,11 +189,14 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.3, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-watch (2.2.1)
|
||||
listen (~> 3.0)
|
||||
jemoji (0.11.1)
|
||||
jemoji (0.12.0)
|
||||
gemoji (~> 3.0)
|
||||
html-pipeline (~> 2.2)
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.0, < 5.0)
|
||||
kramdown (1.17.0)
|
||||
kramdown (2.3.0)
|
||||
rexml
|
||||
kramdown-parser-gfm (1.1.0)
|
||||
kramdown (~> 2.0)
|
||||
liquid (4.0.3)
|
||||
listen (3.2.1)
|
||||
rb-fsevent (~> 0.10, >= 0.10.3)
|
||||
@@ -202,9 +207,9 @@ GEM
|
||||
jekyll (>= 3.5, < 5.0)
|
||||
jekyll-feed (~> 0.9)
|
||||
jekyll-seo-tag (~> 2.1)
|
||||
minitest (5.14.1)
|
||||
minitest (5.14.2)
|
||||
multipart-post (2.1.1)
|
||||
nokogiri (1.10.9)
|
||||
nokogiri (1.10.10)
|
||||
mini_portile2 (~> 2.4.0)
|
||||
octokit (4.18.0)
|
||||
faraday (>= 0.9)
|
||||
@@ -215,7 +220,8 @@ GEM
|
||||
rb-fsevent (0.10.4)
|
||||
rb-inotify (0.10.1)
|
||||
ffi (~> 1.0)
|
||||
rouge (3.19.0)
|
||||
rexml (3.2.4)
|
||||
rouge (3.23.0)
|
||||
ruby-enum (0.8.0)
|
||||
i18n
|
||||
rubyzip (2.3.0)
|
||||
@@ -228,6 +234,8 @@ GEM
|
||||
sawyer (0.8.2)
|
||||
addressable (>= 2.3.5)
|
||||
faraday (> 0.8, < 2.0)
|
||||
simpleidn (0.1.1)
|
||||
unf (~> 0.1.4)
|
||||
terminal-table (1.8.0)
|
||||
unicode-display_width (~> 1.1, >= 1.1.1)
|
||||
thread_safe (0.3.6)
|
||||
@@ -235,8 +243,11 @@ GEM
|
||||
ethon (>= 0.9.0)
|
||||
tzinfo (1.2.7)
|
||||
thread_safe (~> 0.1)
|
||||
unf (0.1.4)
|
||||
unf_ext
|
||||
unf_ext (0.0.7.7)
|
||||
unicode-display_width (1.7.0)
|
||||
zeitwerk (2.3.0)
|
||||
zeitwerk (2.4.0)
|
||||
|
||||
PLATFORMS
|
||||
ruby
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,22 +11,38 @@ sections:
|
||||
url: /odrivetool
|
||||
- title: Parameters & Commands
|
||||
url: /commands
|
||||
- title: Interfaces
|
||||
url: /interfaces
|
||||
- title: Encoders
|
||||
url: /encoders
|
||||
- title: Homing & Endstops
|
||||
url: /endstops
|
||||
- title: Thermistors
|
||||
url: /thermistors
|
||||
- title: Control & Tuning
|
||||
url: /control
|
||||
- title: Troubleshooting
|
||||
url: /troubleshooting
|
||||
- title: Specifications
|
||||
url: /specifications
|
||||
- title: Tutorials
|
||||
docs:
|
||||
- title: Hoverboard Guide
|
||||
url: /hoverboard
|
||||
- title: Migration Guide
|
||||
url: /migration
|
||||
- title: Interfaces
|
||||
docs:
|
||||
- title: Pinout
|
||||
url: /pinout
|
||||
- title: Native Protocol
|
||||
url: /native-protocol
|
||||
- title: CAN Protocol
|
||||
url: /can-protocol
|
||||
- title: ASCII Protocol
|
||||
url: /ascii-protocol
|
||||
- title: Step & Direction
|
||||
url: /step-direction
|
||||
- title: RC PWM
|
||||
url: /rc-pwm
|
||||
- title: Homing & Endstops
|
||||
url: /endstops
|
||||
- title: Thermistors
|
||||
url: /thermistors
|
||||
- title: API Reference
|
||||
- title: For ODrive Developers
|
||||
docs:
|
||||
|
||||
0
docs/analog-input.md
Normal file
0
docs/analog-input.md
Normal file
@@ -12,6 +12,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
The ODrive does not echo commands. That means that when you type commands into a program like `screen`, the characters you type won't show up in the console.
|
||||
|
||||
### Arduino
|
||||
There is an Arduino library that gives some examples on how to use the ASCII protocol to communicate with the ODrive. Check it out [here](../Arduino/ODriveArduino).
|
||||
|
||||
## Command format
|
||||
|
||||
The ASCII protocol is human-readable and line-oriented, with each line having the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -268,6 +268,8 @@ python ../Firmware/interface_generator_stub.py --definitions ../Firmware/odrive-
|
||||
bundle exec jekyll serve --incremental --host=0.0.0.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu 18.04, prerequisites are: `ruby ruby-dev zlib1g-dev`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Releases
|
||||
|
||||
We use GitHub Releases to provide firmware releases.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,6 +51,17 @@ Sometimes you would like the index search to only happen in a particular directi
|
||||
|
||||
*IMPORTANT:* Your motor should find the same rotational position when the ODrive performs an index search if the index signal is working properly. This means that the motor should spin, and stop at the same position if you have set <axis>.config.startup_encoder_index_search so the search starts on reboot, or you if call the command:<axis>.requested_state = AXIS_STATE_ENCODER_INDEX_SEARCH after reboot. You can test this. Send the reboot() command, and while it's rebooting turn your motor, then make sure the motor returns back to the correct position each time when it comes out of reboot. Try this procedure a couple of times to be sure.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hall Effect Encoders
|
||||
Hall effect encoders can also be used with ODrive. The encoder CPR should be set to `6 * <# of motor pole pairs>`. Due to the low resolution of hall effect encoders compared to other types of encoders, low speed performance will be worse than other encoder types.
|
||||
|
||||
When the encoder mode is set to hall feedback, the pinout on the encoder port is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
| Label on ODrive | Hall feedback |
|
||||
|-----------------|---------------|
|
||||
| A | Hall A |
|
||||
| B | Hall B |
|
||||
| Z | Hall C |
|
||||
|
||||
### Startup sequence notes
|
||||
The following are variables that MUST be set up for your encoder configuration. Your values will vary depending on your encoder:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ To launch the main interactive ODrive tool, type `odrivetool` <kbd>Enter</kbd>.
|
||||
It should look something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ODrive control utility v0.4.0
|
||||
ODrive control utility v0.5.1
|
||||
Please connect your ODrive.
|
||||
Type help() for help.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -200,6 +200,9 @@ This is the number of **magnet poles** in the rotor, **divided by two**. To find
|
||||
A good way to find the number of pole pairs is with a current limited power supply. Connect any two of the three phases to a power supply outputting around 2A, spin the motor by hand, and count the number of detents. This will be the number of pole pairs. If you can't distinguish the detents from the normal cogging present when the motor is disconnected, increase the current.
|
||||
Another way is sliding a loose magnet in your hand around the rotor, and counting how many times it stops. This will be the number of _pole pairs_. If you use a ferrous piece of metal instead of a magnet, you will get the number of _magnet poles_.
|
||||
|
||||
`odrv0.axis0.motor.config.torque_constant`
|
||||
This is the ratio of torque produced by the motor per Amp of current delivered to the motor. This should be set to **8.27 / (motor KV)**.
|
||||
|
||||
`odrv0.axis0.motor.config.motor_type`
|
||||
This is the type of motor being used. Currently two types of motors are supported: High-current motors (`MOTOR_TYPE_HIGH_CURRENT`) and gimbal motors (`MOTOR_TYPE_GIMBAL`).
|
||||
<details><summary markdown="span">Which <code>motor_type</code> to choose?</summary><div markdown="block">
|
||||
@@ -370,7 +373,7 @@ The watchdog is fed using the `axis.watchdog_feed()` method of each axis.
|
||||
You can now:
|
||||
* [Properly tune](control.md) the motor controller to unlock the full potential of the ODrive.
|
||||
* See what other [commands and parameters](commands.md) are available, in order to better control the ODrive.
|
||||
* Control the ODrive from your own program or hook it up to an existing system through one of it's [interfaces](interfaces.md).
|
||||
* Control the ODrive from your own program or hook it up to an existing system through one of it's [interfaces](pinout.md).
|
||||
* See how you can improve the behavior during the startup procedure, like [bypassing encoder calibration](encoders.md#encoder-with-index-signal).
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any issues or any questions please get in touch. The [ODrive Community](https://discourse.odriverobotics.com/) warmly welcomes you.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ You may wire the motor phases in any order into a motor connector on the ODrive,
|
||||
| Green | Z |
|
||||
| Black | GND |
|
||||
|
||||
Note: In order to ber compatible with encoder inputs, the ODrive doesn't have any filtering capacitors on the pins where the hall sensors connect. Therefore to get a reliable hall signal, it is recommended that you add some filter capacitors to these pins. You can see instructions [here](https://discourse.odriverobotics.com/t/encoder-error-error-illegal-hall-state/1047/7?u=madcowswe).
|
||||
Note: In order to be compatible with encoder inputs, the ODrive doesn't have any filtering capacitors on the pins where the hall sensors connect. Therefore to get a reliable hall signal, it is recommended that you add some filter capacitors to these pins. You can see instructions [here](https://discourse.odriverobotics.com/t/encoder-error-error-illegal-hall-state/1047/7?u=madcowswe).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Hoverboard motor configuration
|
||||
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ odrv0.axis0.motor.config.requested_current_range = 25 #Requires config save and
|
||||
odrv0.axis0.motor.config.current_control_bandwidth = 100
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the encoder to hall mode (instead of incremental). See the [pinout](interfaces.md#hall-feedback-pinout) for instructions on how to plug in the hall feedback.
|
||||
Set the encoder to hall mode (instead of incremental). See the [pinout](encoders.md#hall-effect-encoders) for instructions on how to plug in the hall feedback.
|
||||
The hall feedback has 6 states for every pole pair in the motor. Since we have 15 pole pairs, we set the cpr to 15*6 = 90.
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
odrv0.axis0.encoder.config.mode = ENCODER_MODE_HALL
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ odrv0.axis0.requested_state = AXIS_STATE_IDLE
|
||||
Hopefully you got your motor to spin! Feel free to repeat all of the above for the other axis if appropriate.
|
||||
|
||||
### PWM input
|
||||
If you want to drive your hoverboard wheels around with an RC remote control you can use the [RC PWM input](interfaces.md#rc-pwm-input). There is more information in that link.
|
||||
If you want to drive your hoverboard wheels around with an RC remote control you can use the [RC PWM input](rc-pwm.md). There is more information in that link.
|
||||
Lets use GPIO 3/4 for the velocity inputs so that we don't have to disable UART.
|
||||
Then let's map the full stick range of these inputs to some suitable velocity setpoint range.
|
||||
We also have to reboot to activate the PWM input.
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/migration.md
Normal file
41
docs/migration.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
# Migration Guide
|
||||
|
||||
Certain changes occurred between firmware versions v0.4.12 and v0.5.1 that will break existing configurations. This document is a guide for how to take a working v0.4.12 ODrive config and change it to work with firmware v0.5.1.
|
||||
|
||||
## Unit Changes
|
||||
ODrive now uses units of [turns], [turns/s], and [turns/s^2] instead of [counts], [counts/s], and [counts/s^2]. In addition, the motor controller class now has an input command of torque in [Nm] instead of current in [Amps]. In general, every user-facing parameter that has to do with position or velocity is affected by the unit change.
|
||||
|
||||
## Control Parameter Names
|
||||
ODrive now uses `input_pos`, `input_vel`, and `input_torque` as commands instead of `pos_setpoint`, `vel_setpoint`, and `current_setpoint`
|
||||
|
||||
## Guide
|
||||
For a working v0.4.12 ODrive configuration, use the following equations to convert parameters as required.
|
||||
|
||||
- `pos_gain` is unaffected ( [counts/s / count] -> [turns/s / turns] )
|
||||
- `vel_gain` is `vel_gain_old` * `torque_constant` * `encoder cpr`
|
||||
- `vel_integrator_gain` is `vel_integrator_gain_old` * `torque_constant` * `encoder cpr`
|
||||
|
||||
For other values, [turns] = [counts] / [encoder cpr]. Converting [counts/s] and [counts/s^2] is similar.
|
||||
|
||||
### Affected Variables
|
||||
- `axis.controller.input_pos`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.input_vel`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.input_torque`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.vel_limit`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.vel_ramp_rate`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.current_ramp_rate` is now `axis.controller.config.torque_ramp_rate`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.circular_setpoint_range`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.inertia`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.config.homing_speed`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.pos_setpoint`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.vel_setpoint`
|
||||
- `axis.controller.torque_setpoint` instead of `axis.controller.current_setpoint`
|
||||
- `axis.trap_traj.config.vel_limit`
|
||||
- `axis.trap_traj.config.accel_limit`
|
||||
- `axis.trap_traj.config.decel_limit`
|
||||
- `axis.encoder.pos_estimate`
|
||||
- `axis.encoder.pos_estimate_circular`
|
||||
- `axis.encoder.vel_estimate`
|
||||
- `axis.config.counts_per_step` is now `turns_per_step` for the step/direction interface
|
||||
- `axis.sensorless_estimator.vel_estimate` is in mechanical [turns/s] instead of electrical [radians/s]
|
||||
|
||||
21
docs/native-protocol.md
Normal file
21
docs/native-protocol.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
# Native Protocol
|
||||
|
||||
This protocol is what the ODrive Tool uses to talk to the ODrive. If you have a choice, this is the recommended protocol for all applications. The native protocol runs on USB and can also be configured to run on UART.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Python
|
||||
|
||||
The ODrive Tool you installed as part of the [Getting Started guide](getting-started.md#downloading-and-installing-tools) comes with a library that you can use to easily control the ODrive from Python.
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you already installed the odrive library (`pip install odrive`), the simplest program to control the ODrive is this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import odrive
|
||||
odrv0 = odrive.find_any()
|
||||
print(str(odrv0.vbus_voltage))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For a more comprehensive example, see [tools/odrive_demo.py](../tools/odrive_demo.py).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Other languages
|
||||
|
||||
We don't have an official library for you just yet. Check the community, there might be someone working on it. If you want to write a library yourself, refer to the [native protocol specification](protocol). You are of course welcome to contribute it back.
|
||||
35
docs/pinout.md
Normal file
35
docs/pinout.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
# Pinout
|
||||
|
||||
| GPIO | primary | step/dir | other |
|
||||
|-----------|-----------|---------------|-------------------------|
|
||||
| GPIO1 | UART TX | Axis0 Step | Analog input, PWM input |
|
||||
| GPIO2 | UART RX | Axis0 Dir | Analog input, PWM input |
|
||||
| GPIO3 | | Axis1 Step (+)| Analog input, PWM input |
|
||||
| GPIO4 | | Axis1 Dir (+) | Analog input, PWM input |
|
||||
| GPIO5 | | | Analog input (*) |
|
||||
| GPIO6 (*) | | | |
|
||||
| GPIO7 (*) | | Axis1 Step (*)| |
|
||||
| GPIO8 (*) | | Axis1 Dir (*) | |
|
||||
|
||||
(+) on ODrive v3.4 and earlier <br>
|
||||
(*) ODrive v3.5 and later
|
||||
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
* You must also connect GND between ODrive and your other board.
|
||||
* ODrive v3.3 and onward have 5V tolerant GPIO pins.
|
||||
* ODrive v3.5 and later have some noise suppression filters on the default step/dir pins
|
||||
* You can change the step/dir pins using `axis.config.<step/dir>_gpio_pin`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pin function priorities
|
||||
1. PWM in, if enabled. Disabled by default.
|
||||
1. UART, **Enabled by default**.
|
||||
1. Step/Dir, if enabled. Disabled by default.
|
||||
1. Analog, default behavior if not overridden (only on supported pins).
|
||||
1. Digital in, default behavior on pins not capable of analog input.
|
||||
|
||||
For predictable results, try to have only one feature enabled for any one pin. When changing pin assignments you must:
|
||||
* `odrv0.save_configuration()`
|
||||
* `odrv0.reboot()`
|
||||
|
||||
### Analog input
|
||||
Analog inputs can be used to measure voltages between 0 and 3.3V. Odrive uses a 12 bit ADC (4096 steps) and so has a maximum resolution of 0.8 mV. Some GPIO pins require the appropriate pin priority (see above) to be set before they can be used as an analog input. To read the voltage on GPIO1 in odrive tool the following would be entered: `odrv0.get_adc_voltage(1)`
|
||||
25
docs/rc-pwm.md
Normal file
25
docs/rc-pwm.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
# RC PWM input
|
||||
You can control the ODrive directly from an hobby RC receiver.
|
||||
|
||||
Some GPIO pins can be used for PWM input, if they are not allocated to other functions. For example, you must disable the UART to use GPIO 1,2. See the [pin function priorities](pinout.md#pin-function-priorities) for more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
Any of the numerical parameters that are writable from the ODrive Tool can be hooked up to a PWM input.
|
||||
As an example, we'll configure GPIO4 to control the angle of axis 0. We want the axis to move within a range of -2 to 2 turns.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Make sure you're able control the axis 0 angle by writing to `odrv0.axis0.controller.input_pos`. If you need help with this follow the [getting started guide](getting-started.md).
|
||||
2. If you want to control your ODrive with the PWM input without using anything else to activate the ODrive, you can configure the ODrive such that axis 0 automatically goes operational at startup. See [here](commands.md#startup-procedure) for more information.
|
||||
3. In ODrive Tool, configure the PWM input mapping
|
||||
```
|
||||
In [1]: odrv0.config.gpio4_pwm_mapping.min = -2
|
||||
In [2]: odrv0.config.gpio4_pwm_mapping.max = 2
|
||||
In [3]: odrv0.config.gpio4_pwm_mapping.endpoint = odrv0.axis0.controller._remote_attributes['input_pos']
|
||||
```
|
||||
Note: you can disable the input by setting `odrv0.config.gpio4_pwm_mapping.endpoint = None`
|
||||
4. Save the configuration and reboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
In [4]: odrv0.save_configuration()
|
||||
In [5]: odrv0.reboot()
|
||||
```
|
||||
5. With the ODrive powered off, connect the RC receiver ground to the ODrive's GND and one of the RC receiver signals to GPIO4. You may try to power the receiver from the ODrive's 5V supply if it doesn't draw too much power. Power up the the RC transmitter. You should now be able to control axis 0 from one of the RC sticks.
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to setup the Failsafe feature on your RC Receiver so that if connection is lost between the remote and the receiver, the receiver outputs 0 for the velocity setpoint of both axes (or whatever is safest for your configuration). Also note that if the receiver turns off (loss of power, etc) or if the signal from the receiver to the ODrive is lost (wire comes unplugged, etc), the ODrive will continue the last commanded velocity setpoint. There is currently no timeout function in the ODrive for PWM inputs.
|
||||
29
docs/specifications.md
Normal file
29
docs/specifications.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<!--- page to show specifications --->
|
||||
# Specifications
|
||||
|
||||
## Electrical Specifications
|
||||
Besides the input voltage range, (12V to 24V for ODrive v3.6 24V, 12V to 56V for ODrive v3.6 56V), the electrical specifications of both version of ODrive v3.6 are the same.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: ODrive versions after v3.5 are closed-source with respect to board files and schematics.
|
||||
### ODrive v3.6 24V and 56V
|
||||
- Peak current per motor: 120 Amps
|
||||
- Max continuous current depends on cooling. See [this](https://discourse.odriverobotics.com/t/odrive-mosfet-temperature-rise-measurements-using-the-onboard-thermistor/972) for more details.
|
||||
- Heatsink in still air: 40A per channel
|
||||
- Heatsink with basic fan cooling: 75A per channel
|
||||
- Heatsing with overkill fan cooling: 90A per channel
|
||||
- Max motor RPM: This depends on your power supply voltage, motor, and encoder. It is the lesser of:
|
||||
- motor RPM limit
|
||||
- encoder RPM limit
|
||||
- motor KV * 0.7 * Supply voltage
|
||||
- 35000 eRPM / # of motor pole pairs
|
||||
- (840M counts/minute) / encoder counts per revolution (for incremental encoders - 4 x pulses per revolution).
|
||||
|
||||
### Schematic
|
||||
The electrical schematic for ODrive v3.5 is available [here](https://github.com/madcowswe/ODriveHardware/blob/master/v3/v3.5docs/schematic_v3.5.pdf) in PDF format.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mechanical Specifications
|
||||
### STEP file
|
||||
A step file for ODrive v3.5 is available [here](https://github.com/madcowswe/ODriveHardware/blob/master/v3/v3.5docs/PCB_v3.5.step)
|
||||
|
||||
### Board outline and mounting hole dimensions
|
||||
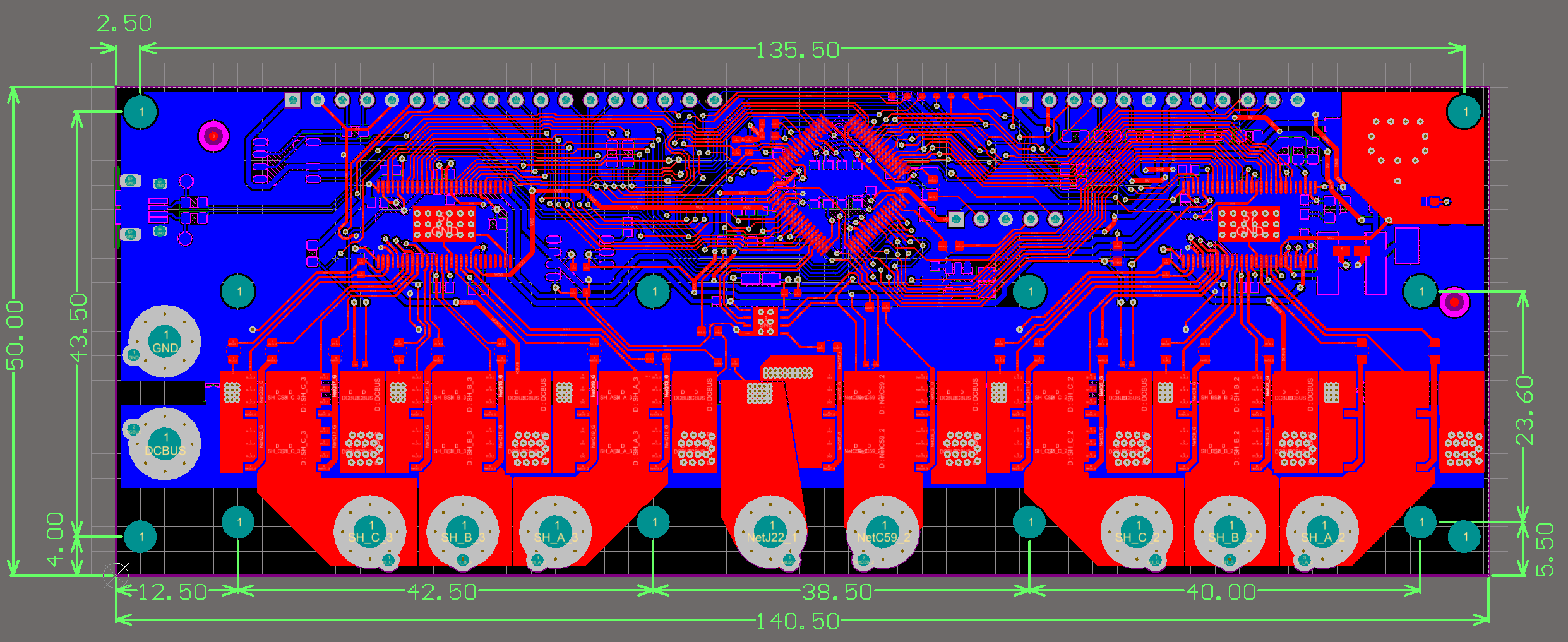
|
||||
14
docs/step-direction.md
Normal file
14
docs/step-direction.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
# Step/direction
|
||||
This is the simplest possible way of controlling the ODrive. It is also the most primitive and fragile one. So don't use it unless you must interoperate with other hardware that you don't control.
|
||||
|
||||
Pinout:
|
||||
* Step/dir signals: see [Pinout](pinout.md). Note in that section how to reassign the pins.
|
||||
* GND: you must connect the grounds of the devices together. Use any GND pin on J3 of the ODrive.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable step/dir mode for the GPIO, set `<axis>.config.enable_step_dir` to true for each axis that you wish to use this on.
|
||||
Axis 0 step/dir pins conflicts with UART, and the UART takes priority. So to be able to use step/dir on Axis 0, you must also set `odrv0.config.enable_uart = False`. See the [pin function priorities](pinout.md#pin-function-priorities) for more detail. Don't forget to save configuration and reboot.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a config variable called `<axis>.config.turns_per_step`, which specifies how many turns a "step" corresponds to. The default value is 1.0f/1024.0f. It can be any floating point value.
|
||||
The maximum step rate is pending tests, but it should handle at least 50kHz. If you want to test it, please be aware that the failure mode on too high step rates is expected to be that the motors shuts down and coasts.
|
||||
|
||||
Please be aware that there is no enable line right now, and the step/direction interface is enabled by default, and remains active as long as the ODrive is in position control mode. To get the ODrive to go into position control mode at bootup, see how to configure the [startup procedure](commands.md#startup-procedure).
|
||||
@@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ The temperature of the onboard FET thermistors can be read out by using the `odr
|
||||
To use your own thermistors with the ODrive a few things have to be clarified first. The use of your own thermistor requires one analog input pin. Under `<axis>.motor_thermistor.config` the configuration of your own thermistor is available with the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
* `gpio_pin`: The GPIO input in used for this thermistor.
|
||||
* `poly_coefficient_0` to `poly_coefficient_3`: Coefficient that needs to be set for your specific setup more on that in [Thermistor coefficients](#Thermistor coefficients).
|
||||
* `poly_coefficient_0` to `poly_coefficient_3`: Coefficient that needs to be set for your specific setup more on that in [Thermistor coefficients](#thermistor-coefficients).
|
||||
* `temp_limit_lower` and `temp_limit_upper`: Same principle as the FET temperature limits.
|
||||
* `enabled`: Whether this thermistor is enabled or not.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,6 +20,34 @@ With this information you can look up the API documentation for your error(s):
|
||||
* Controller error flags documented [here](api/odrive.controller.error).
|
||||
* Sensorless estimator error flags documented [here](odrive.sensorlessestimator.error).
|
||||
|
||||
### What if `dump_errors()` gives me python errors?
|
||||
If you get output like this:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
In [1]: dump_errors(odrv0)
|
||||
axis0
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
|
||||
~/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/fibre/shell.py in <module>
|
||||
----> 1 dump_errors(odrv0)
|
||||
|
||||
~/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/odrive/utils.py in dump_errors(odrv, clear)
|
||||
78 ('axis', axis, {k: v for k, v in odrive.enums.__dict__ .items() if k.startswith("AXIS_ERROR_")}),
|
||||
79 ('motor', axis.motor, {k: v for k, v in odrive.enums.__dict__ .items() if k.startswith("MOTOR_ERROR_")}),
|
||||
---> 80 ('fet_thermistor', axis.fet_thermistor, {k: v for k, v in odrive.enums.__dict__ .items() if k.startswith("THERMISTOR_CURRENT_LIMITER_ERROR")}),
|
||||
81 ('motor_thermistor', axis.motor_thermistor, {k: v for k, v in odrive.enums.__dict__ .items() if k.startswith("THERMISTOR_CURRENT_LIMITER_ERROR")}),
|
||||
82 ('encoder', axis.encoder, {k: v for k, v in odrive.enums.__dict__ .items() if k.startswith("ENCODER_ERROR_")}),
|
||||
|
||||
~/.local/lib/python3.6/site-packages/fibre/remote_object.py in __getattribute__(self, name)
|
||||
243 return attr
|
||||
244 else:
|
||||
--> 245 return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
|
||||
246 #raise AttributeError("Attribute {} not found".format(name))
|
||||
247
|
||||
|
||||
AttributeError: 'RemoteObject' object has no attribute 'fet_thermistor'
|
||||
```
|
||||
when you call `dump_errors()`, you have a version mismatch between odrivetool and the firmware on your ODrive. To get the newest version of odrivetool, you can run `pip install odrive --upgrade`. To get the newest ODrive firmware, run `odrivetool dfu`. See the [odrivetool](odrivetool.md#device-firmware-update) page for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## USB Connectivity Issues
|
||||
|
||||
* Try turning it off and on again (the ODrive, the script, the PC)
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user